Detect water absorption quickly and reliably with NIR
Water absorption is often desirable with PA, as it increases the impact strength. However, without being able to determine the water content quickly and reliably, the processing effort increases. NIR reliably distinguishes polymers with different water contents in seconds.
Polyamides: Water absorption causes problems with dimensional stability
Polyamides can be used in many different ways. PA6 and PA66 in particular can significantly improve their properties by adding certain substances. When water is absorbed, the impact strength, elongation at break and tendency to creep increase, while strength, stiffness and hardness decrease. However, moisture absorption is accompanied by a change in volume which leads to problems with dimensional stability. If the water content changes, the measurement changes. Determining the water content is essential for correct processing. However, the storage of plastics in the open air or in humid climates in particular leads to unknown changes in the water content.
How to distinguish PA with different water content?
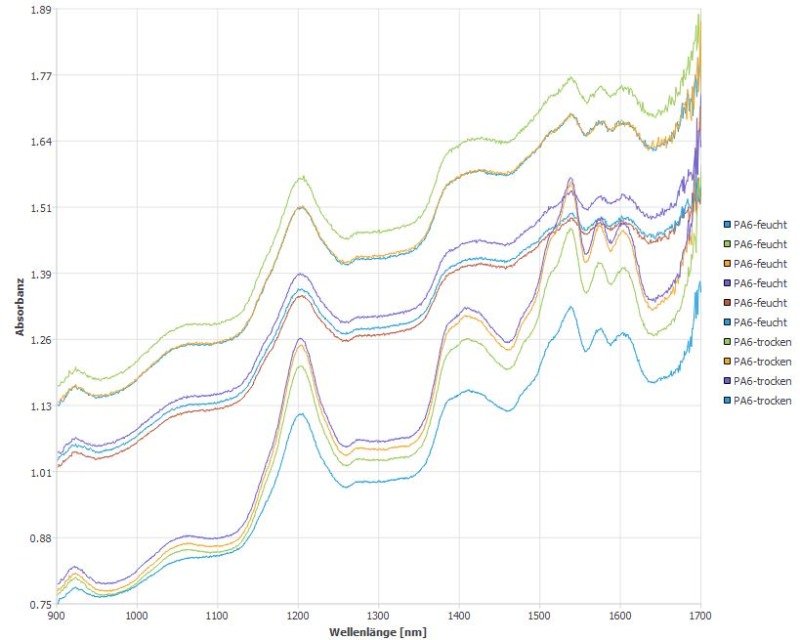
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) is a method that can be used to differentiate between plastics with different moisture contents in a matter of seconds. NIR is an optical method that converts the light reflected by the material under investigation into a spectrum. Depending on the chemical composition of the polymer, different wavelengths are reflected. If the chemical composition changes, the measured spectrum changes. Near-infrared spectroscopy is therefore a method that produces results in just a few seconds.
NIR reliably detects moisture
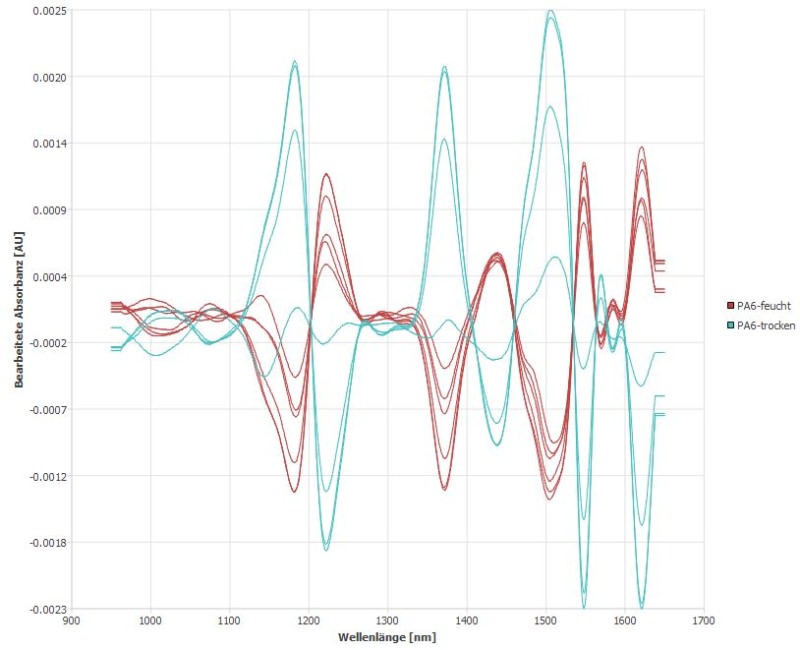
NIR works in the wavelength range from 900 nm to 1,700 nm. Water influences the signals in the range from 1,200 nm to 1,400 nm, it attenuates the actual signal of the polyamide. Because water changes the NIR signal over such a wide range, even the smallest differences in water content lead to strong differences in the NIR signal. This means that even small differences in moisture absorption can be reliably detected.
Moisture absorption of polycarbonate (PC)
Not only polyamides absorb moisture, but also PC and PMMA are susceptible to this problem.
Conclusion
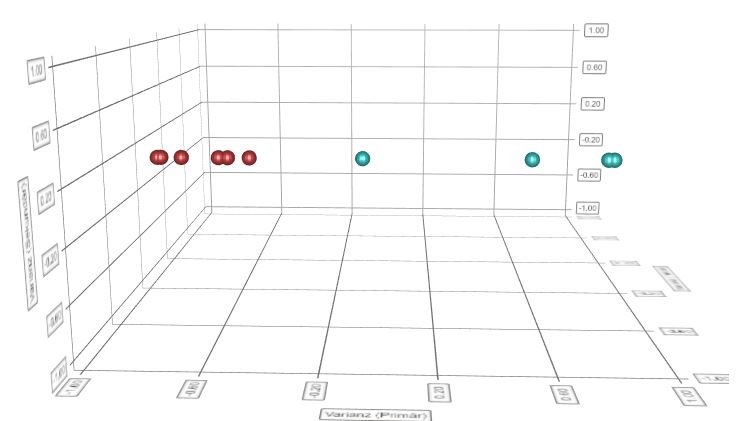
Due to the specific mode of operation of near-infrared, plastics with the smallest differences in moisture content can be quickly and reliably distinguished. The fist-sized NIR scanner Solid Scanner is therefore perfect for differentiating materials directly on site at the storage location or in production. For this example we used Hardware
Software
Reference data